How can you tell the difference between psoriasis and eczema?
Most people are not able to recognize whether it’s psoriasis or eczema (also called atopic dermatitis). The treatment of psoriasis or eczema depends on recognizing the patch of skin that’s inflamed, reddish, or peeling as one of the characteristic symptoms of these conditions. Both of them are skin conditions with almost similar symptoms, but there are differences technically that can differentiate them apart.
What is psoriasis and eczema?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes overproduction of your skin cells. The condition cannot be cured, but there are some topical and oral medicines as well as laser treatments that can relieve the symptoms. Psoriasis isn’t contagious.
Eczema is a common skin disease, particularly in children. Eczema (also called atopic dermatitis) occurs when the skin reacts to certain triggers, such as fabrics, soaps, detergents, scents, animals, chemicals such as makeup products, and other irritants.
Both psoriasis and eczema (dermatitis) can occur anywhere on the body and causes itching. Eczema can be treated with topical treatment in most cases.
Comparing psoriasis and eczema: What is the difference and what are similarities?
Both diseases (psoriasis and eczema) start with the immune system
Both psoriasis and eczema are related to your immune system. In psoriasis, you have an over-reactive immune system that affects a type of white blood cells (called T-cells) that protect you from infections and diseases.
You develop eczema because of a hypersensitivity reaction that causes the skin to overreact to certain triggers or external conditions. It is also caused by a problem with your immune system, but in a different way than psoriasis.
Psoriasis vs. eczema on face
Psoriasis on the face
Psoriasis generally affects the knees and elbows, but it can occur anywhere on the body. It can affect your scalp, face, and neck. While the psoriasis on the face and scalp can be treated with medicines and topical treatment options, but it may recur. Scalp psoriasis can also grow to the forehead, ears, or neck. In such situation, it can be difficult to treat psoriasis.
Psoriasis on the face (called facial psoriasis) can cause a variety of symptoms and complications. But there are many ways to treat it. Psoriasis on face usually occurs when scalp psoriasis extends to the forehead and face. Generally, a person with psoriasis on face has dead skin cells in hair as well (called scalp psoriasis). Many people mistake psoriasis on face as dandruff in the beginning.
Eczema on the face
Just like psoriasis, eczema can also develop on the face can. Eczema on the face is characterized by patches on the skin that can be very itchy. Itching can cause skin breaks that may sometime cause bleeding or infection of the skin. The skin can become dry causing development of cracks.
The characteristic feature of eczema is that pus-filled blisters start forming after a few days of the appearance of rashes/patches. Scratching can cause the skin to ooze pus and create crusty patches. Your doctor will likely recommend topical treatments to treat eczema on the face. Sometimes, other medicines and therapies are also used.
Eczema on scalp (called scalp eczema) in another type of eczema that can resemble psoriasis on head or scalp. Eczema on scalp causes inflamed, itchy, dry skin to form on your scalp. The most common type of scalp eczema is known as seborrheic dermatitis, and one of its symptoms is dandruff.
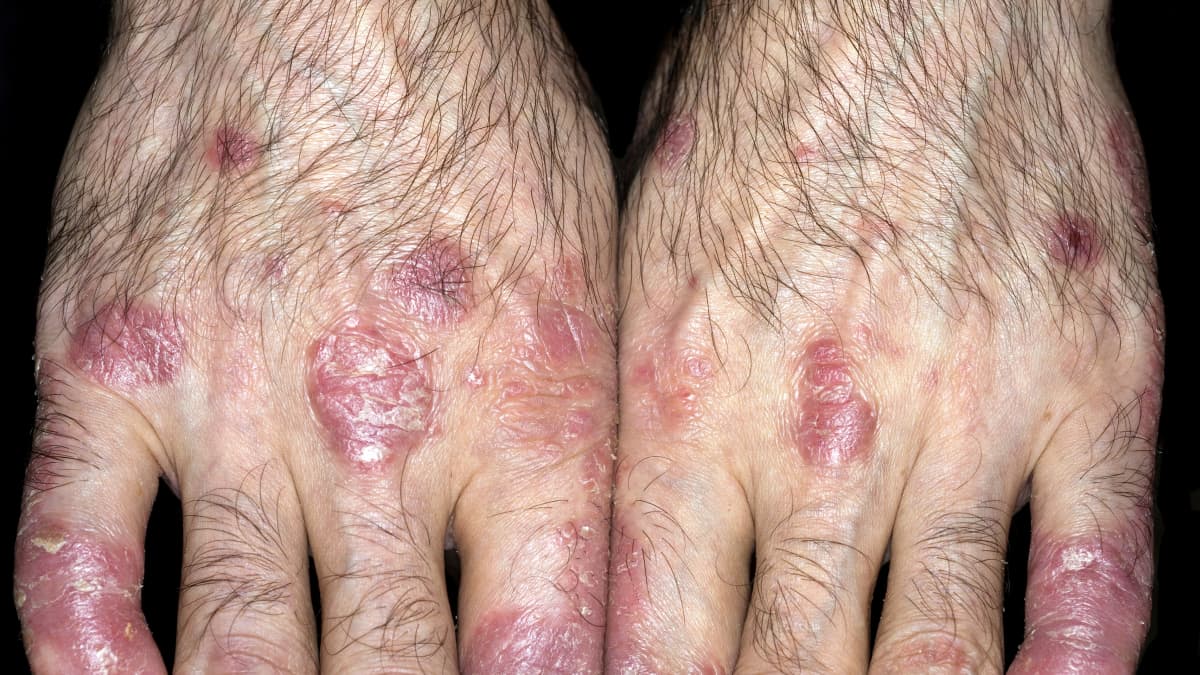
Psoriasis vs. eczema on hands
Psoriasis on hands and fingers
Psoriasis on hands or psoriasis on fingers is a common type of psoriasis. Many people develop patches of psoriasis on the back sides of their hands or in the fingers. Some people get it on their palms. Psoriasis on hands can cause peeling of the skin that becomes dry. Even normal routine tasks such as washing of the hands or picking up things in hands can cause pain. Psoriasis on fingers can be very discomforting particularly when washing hands etc.
Another form of psoriasis on hands is called nail psoriasis. Nail psoriasis causes the skin to produce too many cells under the nails. It can look similar to a fungal infection and can look like discoloration of the nails. Sometimes, nails may fall off the skin. Psoriasis on hands can be treated with topical and other treatments. But it cannot be cured permanently.
Eczema on hands
Eczema on hands is very common. Hands are usually exposed to the environment and common irritants that trigger the symptoms of eczema. Hands often come in contact with for example soaps, lotions, creams, makeup things, fabric, and other allergens or irritants.
Drying of the skin can make the condition worse. Sometimes, due to frequent washing of the hands, the skin can become even drier which can make eczema on hands difficult to treat. In general too, eczema on hands can be difficult to treat because of the contact with water and other irritants constantly.
Psoriasis vs. eczema on legs
Psoriasis on legs
Psoriasis can commonly affect knees, feet, and legs. Some types of psoriasis may cover major portions of the legs, and some others types may appear in selected places as isolated patches only. The different types of psoriasis have different symptoms and appearances.
Guttate psoriasis on the legs, for example, appears as separate patches. On the other hand, plaque psoriasis on the legs generally shows up in large patches with thick red skin or white scales. Psoriasis on feet (called foot psoriasis) can also occur commonly and is very uncomfortable particularly if it affects the soles of your feet.
Eczema on legs
Eczema usually occurs in regions that traps sweat or moisture or other irritants or are rubbed often with clothing or other skin portions etc. Eczema on the legs may develop in body creases such as on the back of the knee or the front of the ankle. These areas may trap sweat or irritants from clothing and have skin-to-skin contact as well. This increases the chances of psoriasis on legs to grow in these areas.
Symptoms of psoriasis VS symptoms of eczema: What do psoriasis and eczema look like?
Eczema causes reddish skin and inflammation. The skin may become scaly with oozing blisters, or crusty skin. You can note rough patches like that of leather on the skin. These patches may become swollen.
Psoriasis may also have certain similar symptoms. Psoriasis may also cause red patches. They may also be scaly, sometimes silvery too. But, these patches caused due to psoriasis are slightly raised higher on the skin. The skin with psoriasis is thicker and more inflamed than that of eczema.
Common locations where psoriasis and eczema symptoms appear
Psoriasis often shows up on:
- Scalp and hair
- Face
- Lower back of the elbows
- Knees, psoriasis on legs
- Palms of the hands
- Soles of the feet (psoriasis on feet)
- Psoriasis on fingers: Fingernails and toenails
- Eyelids
- Psoriasis on ears
- Skin folds
- Mouth and lips
Eczema often affects your:
- Inner portions of the elbows
- Behind the knees
- Neck
- Wrists
- Ankles
- Sometimes on cheeks, particularly in babies
- Legs
Can someone have both psoriasis and eczema?
It’s rare that a person will have both eczema (dermatitis) and psoriasis, but it is possible. According to a research published in the journal Science Translational Medicine that involved patients who had both eczema and psoriasis, the researchers found that people have different genes present in the skin tissue of each condition type that can help the doctors diagnose each condition better.
Other skin conditions that cause similar symptoms
It is true that eczema and psoriasis resemble one another. But there are other skin conditions too that can resemble them. Few examples of these skin conditions that can cause similar symptoms are:
- Hives
- Shingles
- Contact dermatitis
- Rosacea
- Cradle cap (also called Seborrheic dermatitis)
- Athlete’s foot