Introduction
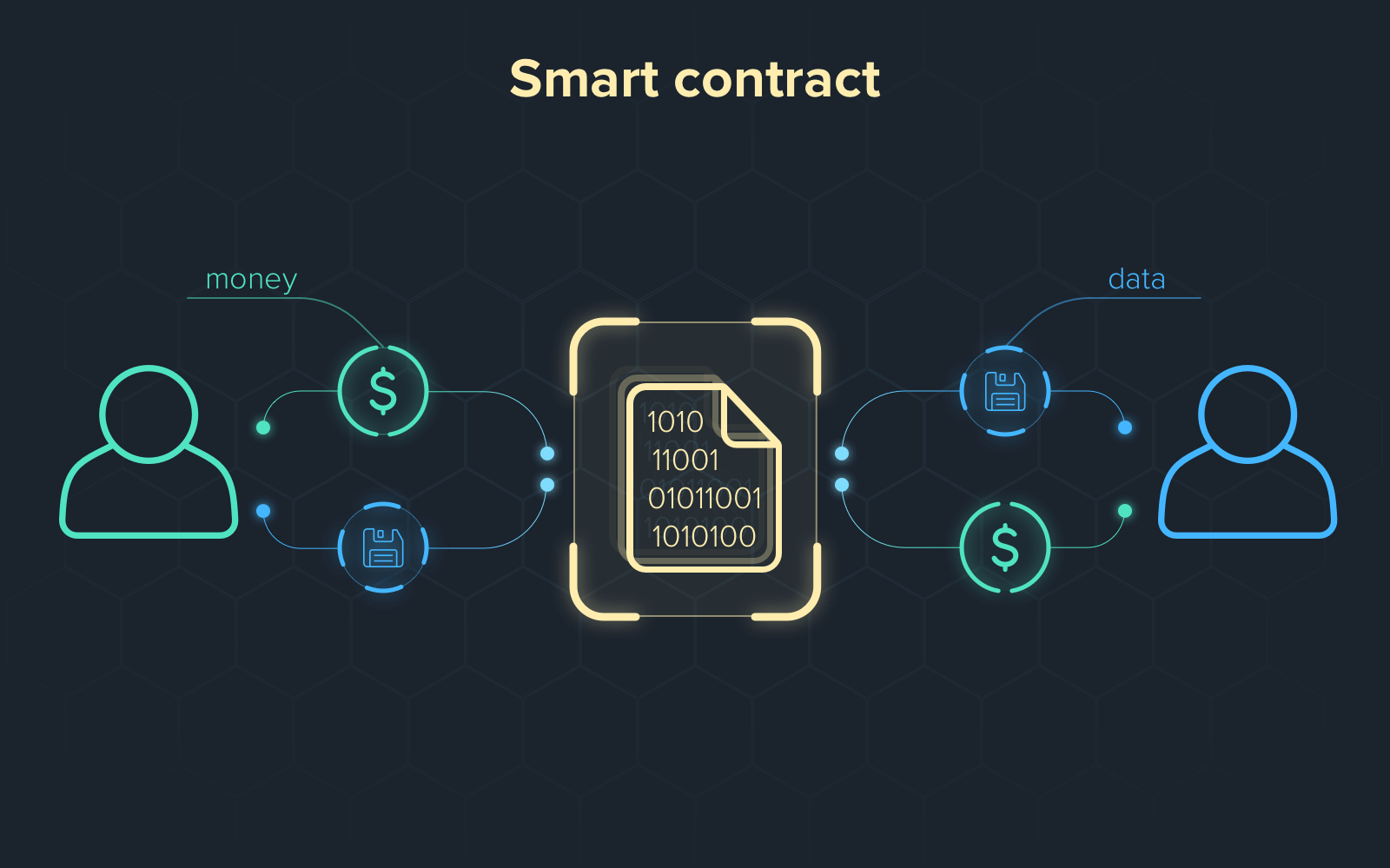
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts built on blockchain technology. They revolutionize how agreements are made and enforced, offering greater transparency, automation, and enhanced security compared to traditional contracts. Let’s explore what they are and their potential impact.
What are Smart Contracts?
- Self-executing code: Smart contracts are computer programs on a blockchain that automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met.
- Immutability: Once deployed on a blockchain, smart contracts cannot be easily tampered with, guaranteeing their execution as designed.
- Trustless: Smart contracts eliminate the need for intermediaries, promoting trustless and transparent transactions.
How Smart Contracts Work?
- Agreement Codified: The terms of a contract are translated into programmable code (e.g., if X occurs, then execute Y).
- Deployment on Blockchain: The smart contract code is deployed onto a secure and decentralized blockchain network like Ethereum.
- Triggering Event: A real-world event or a condition within the blockchain triggers the smart contract’s terms.
- Automatic Execution: The smart contract verifies conditions and executes the predetermined actions, such as transferring funds or updating ownership records.
Use Cases of Smart Contracts
- Supply Chain Management: Smart contracts track goods and payments, ensuring transparency and efficiency.
- Real Estate: Smart contracts automate property transactions, reducing delays and potential disputes.
- Financial Services: Decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols powered by smart contracts enable lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries.
- Voting Systems: Secure, transparent elections using smart contracts on a blockchain enhance the integrity of voting processes.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
- Efficiency: Automation eliminates delays and potential errors of manual contract processes.
- Transparency: Transactions are recorded on the blockchain, providing accountability and auditability.
- Security: Blockchain’s immutability and cryptography make smart contracts highly resistant to fraud.
- Reduced Costs: Eliminating intermediaries can lower transaction costs.
Considerations
- Limitations of Coding: Smart contracts are limited to the way they’re coded. Ambiguities or errors can lead to unintended consequences.
- Legal Framework: Integration of smart contracts into existing legal systems is an evolving area.
- Technological Maturity: Blockchain technology and smart contract development continue to improve and mature.
Conclusion
Smart contracts hold immense potential to reshape agreements in various industries. As the technology advances and addresses current challenges, smart contracts could become a cornerstone of secure and transparent business transactions.